
However, in most modern instruments, solid-state detectors are now used. In the past, photomultiplier tubes have been used as the detector. In general, a different lamp is used for each element to be determined, although in some cases, a few elements may be combined in a multi-element lamp. The light source normally used is a hollow cathode lamp (HCL) or an electrodeless discharge lamp (EDL). Performing atomic absorption spectroscopy requires a primary light source, an atom source, a monochromator to isolate the specific wavelength of light to be measured, a detector to measure the light accurately, electronics to process the data signal and a data display or reporting system to show the results. As the orbital configuration of a large atom may be complex, there are many electronic transitions which can occur, each transition resulting in the emission of a characteristic wavelength of light.
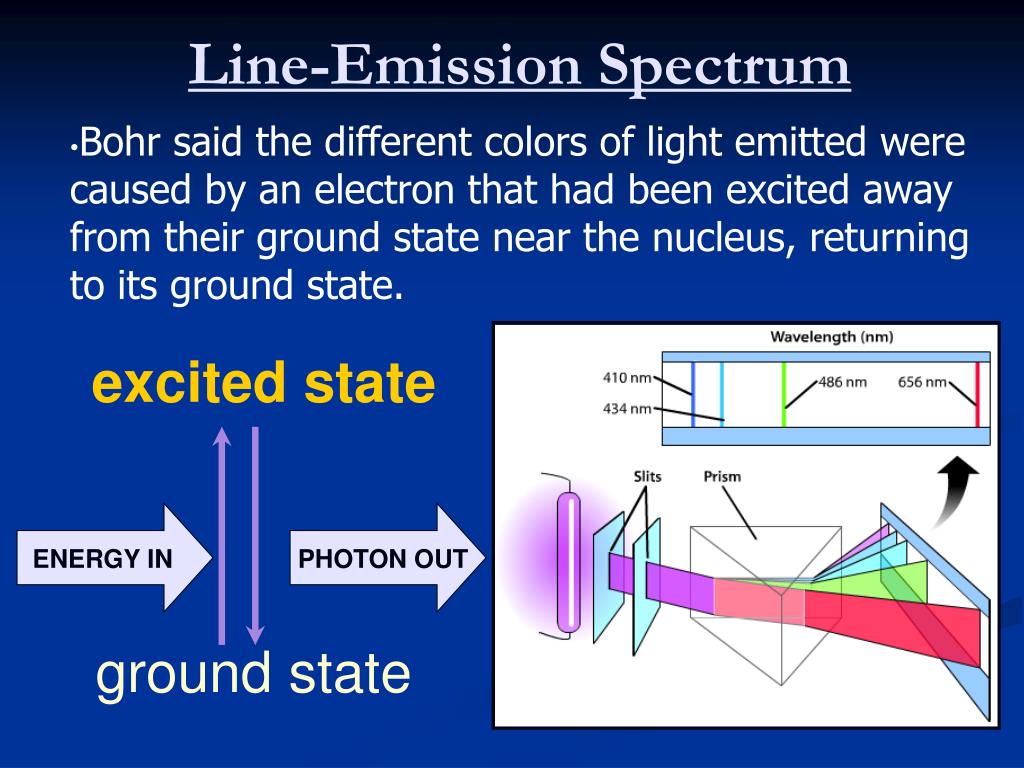
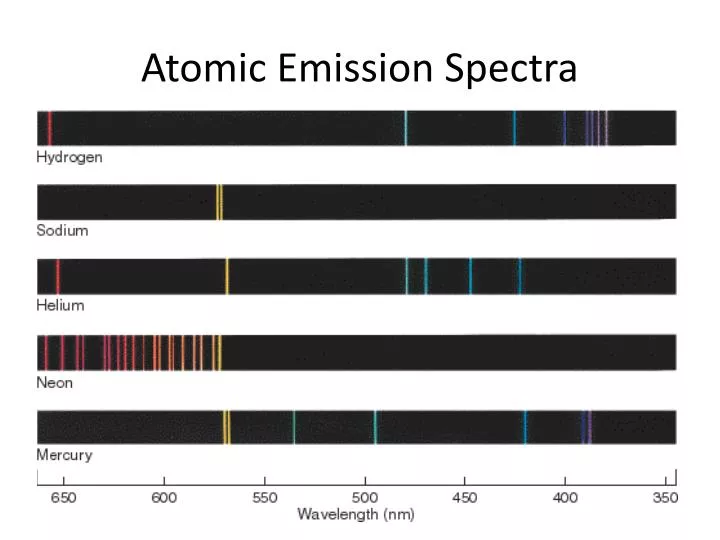
Since every element has a unique electronic structure, the wavelength of light emitted is a unique property of each individual element. The wavelength of the emitted radiant energy is directly related to the electronic transition which has occurred. In optical spectroscopy, the energy absorbed to move an electron to a more energetic level and/or the energy emitted as the electron moves to a less energetic energy level is in the form of a photon. These levels have well defined energies and electrons moving between them must absorb or emit energy equal to the difference between them. Electrons exist in energy levels within an atom. The study of the electromagnetic spectrum of elements is called Optical Atomic Spectroscopy. I think this is when white light is used that you get an Absorption Spectra.The laboratory scientist work with microwave plasma atomic emission spectrometer (MPAES) for elemental property analysis of material sample in all areas of industry.Ītomic spectroscopy is the determination of elemental composition by its electromagnetic or mass spectrum. All the colors of the Absorption Spectra do make it kind of confusing. And these are being absorbed (with emphasis on blue).

Actually, if you just burned hydrogen and looked at its spectra, you would get the Emission Spectra and not the Absorption Spectra, and this Emission Spectra would only show the bunch of blue lines, one purple line, and one red line. All the other colors shown are just part of the natural light being shown down on the element. This is the color that will be the opposite of the flame color on the color wheel. Remember, always look at the color area on the rainbow that is blacked out the most. So if blue is being absorbed, the opposite color would be transmitted and this color is orange. However, there are MORE dark lines in the blue region. If you look at the lines for hydrogen blue, purple, and red are being absorbed. Therefore, all the other colors would be absorbed. (This would be orange.) The element hydrogen turns orange when being burned and this color is transmitted to us. This means that if there is a big dark band where blue would be, then the opposite color to blue on the color wheel is being transmitted. You are supposed to look at the dark areas of the absorption spectra and those dark areas indicate that the color which would be there is being absorbed. I think both the absorption and emission lines are showing which colors are being absorbed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
